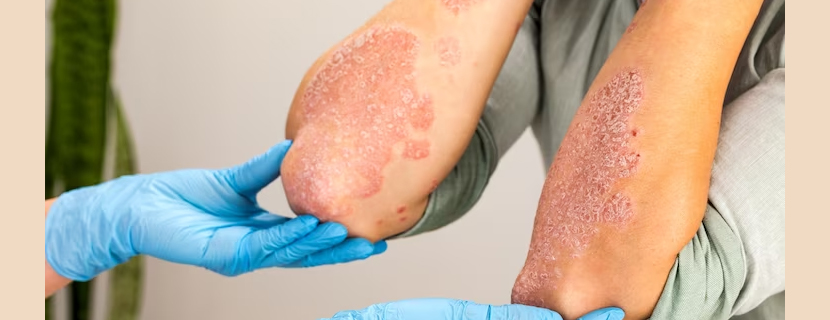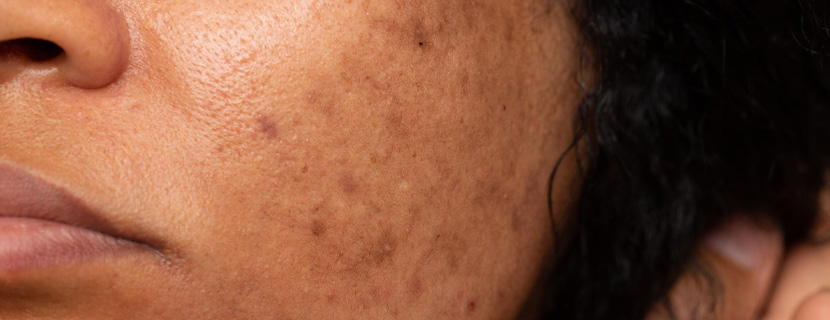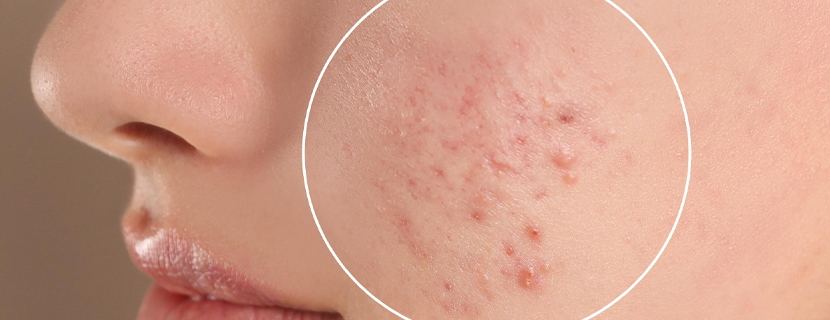
Psoriatic arthritis occurs when your body's immune system attacks healthy cells and tissue. The immune response causes inflammation in your joints as well as overproduction of skin cells. It seems likely that both genetic and environmental factors play a role in this immune system response. Many people with psoriatic arthritis have a family history of either psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis. Researchers have discovered certain genetic markers that appear to be associated with psoriatic arthritis. Physical trauma or something in the environment — such as a viral or bacterial infection — might trigger psoriatic arthritis in people with an inherited tendency.

Scalp psoriasis affects over 60 percent of people living with psoriasis. Scalp psoriasis can affect the hairline, the forehead, the back of the neck and the skin in and around the ears.
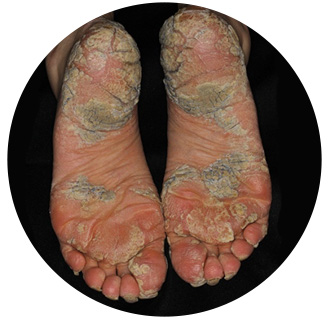
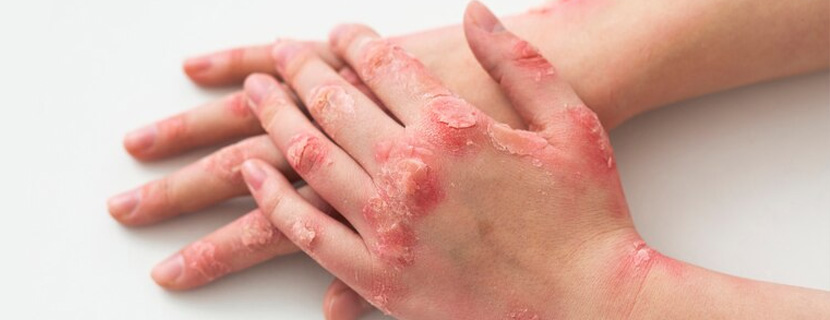
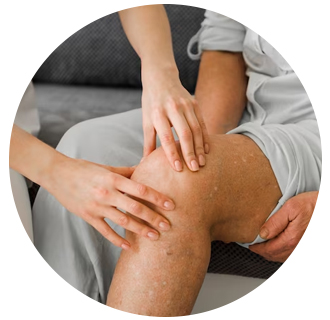
Hands, feet and nails can also be affected by psoriasis. Palmoplantar psoriasis (PPP) refers to psoriasis that affects the palms of the hands and/or the soles of the feet. Between 12 and 16 percent of people living with psoriasis have palmoplantar psoriasis. Nail changes can also occur in 50percent of people living with psoriasis.